
Research Overview
MocoExtendProblem (MEP) is a framework to rapidly develop novel goals for biomechanical optimal control problems using OpenSim Moco and MATLAB. This research addresses the challenge of creating custom optimization goals without requiring extensive C++ development experience.
Project Background
OpenSim is an open-source software platform for modeling musculoskeletal structures and creating dynamic simulations of movement. While OpenSim originally featured single-shooting methods, it now includes Moco which employs direct collocation for solving curve-fitting problems ranging from muscle forces to tracking experimental data and fully predictive simulations.
Direct collocation is a numerical optimal control method that is computationally efficient compared to single-shooting algorithms and is used extensively in computational approaches to understanding biological movement. However, OpenSim Moco only provides a small predefined set of optimization goals, and more sophisticated goals require understanding the C++ API and ability to build custom plugins or rebuild OpenSim from source.
This creates a significant barrier for many biomechanics researchers who lack experience in building software written in C++. MocoExtendProblem was developed to address this challenge, allowing Moco users without C++ experience to write and test custom goals.
Technical Approach
MEP features several key innovations:
Build System
- Automated Compilation: A `build.m` script that compiles goals in the `custom_goals` directory and procedurally constructs C++/MATLAB class implementations
- MEX Interface: Compiles a MEX function using OpenSim's API for MATLAB without requiring OpenSim rebuilds or plugin development
- Version Compatibility: Support for OpenSim versions 4.2-4.5 with unique considerations for different versions
Development Workflow
- Template System: Users copy goal folders as templates and modify them for new custom goals
- Procedural Generation: The build system automatically parses header files and generates necessary bindings
- MATLAB Integration: Custom goals can be easily incorporated into existing MATLAB-OpenSim scripts
Architecture
The framework consists of several key components:
- Build Script: Orchestrates the compilation process and generates interface code
- Utils Folder: Contains methods for reading custom goals and constructing the MEX interface
- Custom Goals: Individual compiled plugins for each custom optimization goal
- ExtendProblem Class: MATLAB wrapper that provides access to custom goals
Research Applications
To demonstrate the utility of MEP, the research team generated a two-dimensional walking simulation using the MATLAB-OpenSim API. The base simulation used built-in MocoControlEffortGoal and MocoAverageSpeedGoal to generate tracking and predictive simulations of minimum effort walking at 1.3 m/s.
Since Moco lacks built-in gait stability goals, three novel stability goals were developed using MEP:
Stability Goals
- Base of Support (BOS): Optimizes whole-body center of mass to lie between the two hindfeet COMs projected to the ground
- Zero-Moment-Point (ZMP): Tracks the computed zero-tilting moment location in the transverse plane
- Marker Acceleration Minimization: Minimizes explicit accelerations of a marker placed on the head
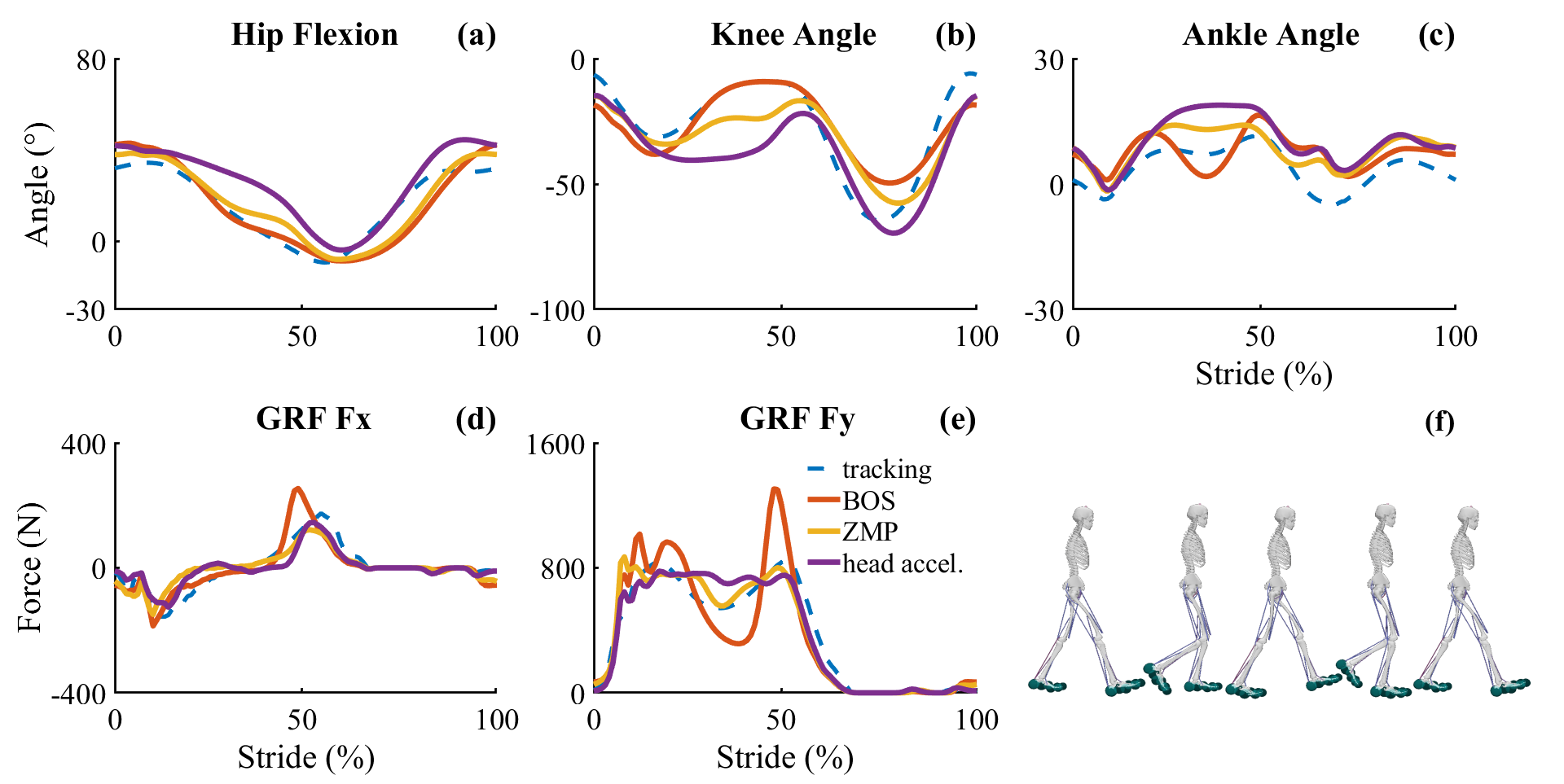
Simulation Results
Results from multi-objective predictive simulations using MEP-compiled stability criteria compared against tracking simulation data. The framework successfully generated stable walking patterns with different optimization objectives.
Technical Implementation
The implementation leverages several key technologies:
Build Requirements
- CMake: Version 3.23.3 or higher for cross-platform build configuration
- Visual Studio: 2019 or higher with C++ desktop development workload
- MATLAB: Version 2022a/b with MEX compiler configured for C++
- OpenSim: Versions 4.2-4.5 with MATLAB scripting environment setup
Integration Process
To incorporate MEP goals into existing MATLAB scripts:
- Obtain a C-style pointer to the instantiated MocoProblem
- Instantiate the procedurally-generated ExtendProblem class
- Use class methods to add custom goals with specified weights and parameters
Research Impact
MocoExtendProblem has significant implications for the biomechanics research community:
- Accessibility: Enables researchers without C++ experience to develop custom optimization goals
- Modularity: Provides a framework for rapidly developing, testing, and comparing novel MocoGoals
- Extensibility: The same strategies can be applied to extend other OpenSim classes
- Version Compatibility: Allows back-porting goals from newer OpenSim versions to older ones
Current Applications
MEP is currently being used successfully in ongoing research of locomotor performance in humans and other animals. The framework is agnostic to model complexity or task, making it suitable for a wide range of biomechanical applications beyond the demonstrated planar gait simulations.
Publication and Resources
This research has been published and all tools, instructions, and simulation results are available on:
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation (BCS 2018436 and BCS 2018523).

