Project Overview
The Lua Godot Bridge is a sophisticated C++ GDExtension that seamlessly integrates Lua scripting capabilities into Godot 4 games and applications. This framework provides a powerful bridge between Godot's native C++ engine and Lua's lightweight, fast scripting language, enabling dynamic modding, runtime script execution, and flexible game logic implementation.
The project addresses the growing need for modding support in modern game development by providing a robust, sandboxed environment where Lua scripts can interact safely with Godot objects, while maintaining performance and security standards expected in production environments.
Core Architecture
GDExtension Integration
The bridge is built as a GDExtension using Godot's C++ bindings, providing native performance while exposing Lua functionality to the Godot scripting environment. The architecture consists of several key components:
- LuaBridge Class: Main interface between Godot and Lua, managing VM lifecycle and data conversion
- Mod Resource Loader: Handles loading and management of Lua mod files and JSON metadata
- Object Wrappers: Provides safe access to Godot objects from Lua scripts
- Event System: Enables communication between Lua scripts and Godot signals
- Sandboxing: Implements security measures to prevent malicious script execution
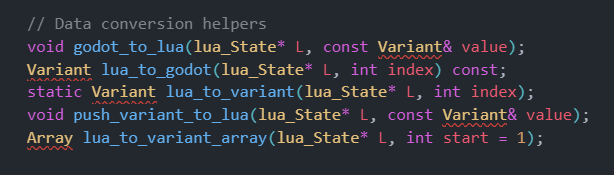
Data Conversion Layer
The bridge implements sophisticated type conversion between Godot's Variant system and Lua's dynamic typing:
// Convert Godot Variant to Lua value
void godot_to_lua(lua_State* L, const Variant& value) {
switch (value.get_type()) {
case Variant::Type::STRING:
lua_pushstring(L, value.operator String().utf8().get_data());
break;
case Variant::Type::INT:
lua_pushinteger(L, value.operator int64_t());
break;
case Variant::Type::FLOAT:
lua_pushnumber(L, value.operator double());
break;
case Variant::Type::ARRAY:
push_array_to_lua(L, value.operator Array());
break;
case Variant::Type::DICTIONARY:
push_dict_to_lua(L, value.operator Dictionary());
break;
default:
lua_pushnil(L);
}
}Key Features
Modding System
The framework includes a comprehensive modding system that supports JSON-based mod metadata and automatic lifecycle management:
{
"name": "ExampleMod",
"version": "1.0.0",
"author": "Example Author",
"description": "An example mod that demonstrates the Lua modding system",
"entry_script": "main.lua",
"enabled": true,
"dependencies": [],
"tags": ["example", "demo"],
"website": "https://example.com/mod",
"license": "MIT"
}Lifecycle Hooks
Lua scripts can implement standard lifecycle hooks for proper initialization and cleanup:
-- Lifecycle hooks for mod management
function on_init()
print("Mod initializing...")
-- Set up initial state
player_position = {x = 100, y = 100}
end
function on_ready()
print("Mod is ready!")
-- Set up event listeners, start timers
end
function on_update(delta)
-- Called every frame with delta time
timer = timer + delta
if timer >= 5.0 then
print("5 seconds have passed!")
timer = 0
end
end
function on_exit()
print("Mod shutting down...")
-- Clean up resources
endGodot Object Integration
Lua scripts can directly access and manipulate Godot objects through the bridge:
-- Access Godot objects from Lua
local player = get_node("/root/Main/Player")
if player then
-- Call Godot methods
call_method(player, "set_position", {100, 200})
-- Get properties
local health = get_property(player, "health")
print("Player health:", health)
-- Connect to signals
connect_signal(player, "damage_taken", "on_player_damaged")
end
-- Signal handler function
function on_player_damaged(damage_amount)
print("Player took", damage_amount, "damage!")
endUsage Examples
Basic Script Execution
The bridge provides simple methods for executing Lua code and managing global variables:
# Initialize the Lua bridge
var lua_bridge = LuaBridge.new()
lua_bridge.initialize()
# Execute Lua code
lua_bridge.exec_string("x = 42; y = 'hello'")
# Set and get global variables
lua_bridge.set_global("game_time", 123.45)
var time = lua_bridge.get_global("game_time")
# Call Lua functions
var result = lua_bridge.call_function("calculate_damage", [100, 1.5, 0.2])Mod Loading and Management
The framework supports automatic mod discovery and loading from directories:
# Load mods from directory
var success = lua_bridge.load_mods_from_directory("res://mods/")
# Get information about loaded mods
var mod_info = lua_bridge.get_all_mod_info()
for mod in mod_info:
print("Mod:", mod["name"], "Version:", mod["version"])
# Enable/disable mods at runtime
lua_bridge.enable_mod("ExampleMod")
lua_bridge.disable_mod("DebugMod")
# Reload a specific mod
lua_bridge.reload_mod("ExampleMod")Event System
The bridge includes an event system for communication between Lua scripts and Godot:
# Emit events from Godot
lua_bridge.emit_event("player_level_up", {"level": 5, "experience": 1000})
# Subscribe to events in Lua
lua_bridge.subscribe_event("player_level_up", "on_level_up")-- Event handler in Lua
function on_level_up(data)
print("Player reached level", data.level)
print("Experience gained:", data.experience)
-- Trigger additional game logic
unlock_new_abilities(data.level)
endTechnical Details
Build System
The project uses a multi-platform build system with support for Windows, Linux, and macOS:
# Build Lua as static library
add_library(lua STATIC ${LUA_SOURCES})
target_include_directories(lua PUBLIC ${LUA_INCLUDE_DIR})
# Build the GDExtension
add_library(lua_bridge SHARED ${EXTENSION_SOURCES})
target_include_directories(lua_bridge PRIVATE
${GODOT_CPP_INCLUDE_DIR}
${GODOT_CPP_GEN_INCLUDE_DIR}
${LUA_INCLUDE_DIR}
)
# Link libraries
target_link_libraries(lua_bridge lua godot-cpp)Security and Sandboxing
The bridge implements comprehensive security measures to prevent malicious script execution:
- Safe Libraries: Only essential Lua libraries are exposed (math, string, table)
- Resource Limits: Memory and execution time limits prevent infinite loops
- Object Validation: All Godot object access is validated before execution
- Error Isolation: Lua errors are caught and handled gracefully
- Function Whitelisting: Only approved Godot functions can be called from Lua
Performance Optimizations
The framework includes several performance optimizations:
| Optimization | Implementation | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Object Caching | Wrappers are cached to avoid repeated object creation | Reduced memory allocation overhead |
| Type Conversion | Efficient Variant-to-Lua conversion with minimal copying | Faster data transfer between systems |
| Lazy Loading | Mods are loaded only when needed | Faster startup times |
| Coroutine Support | Lua coroutines for non-blocking operations | Better frame rate consistency |
Memory Management
The bridge implements proper memory management to prevent leaks:
// Automatic cleanup of Lua objects
class LuaBridge {
private:
lua_State* L = nullptr;
bool is_cleaning_up = false;
public:
~LuaBridge() {
if (L) {
is_cleaning_up = true;
lua_close(L);
L = nullptr;
}
}
void cleanup_coroutines() {
for (auto& pair : coroutine_active) {
pair.second = false;
}
}
};Dependencies
Core Dependencies
- Godot C++: Godot 4.x C++ bindings for GDExtension development
- Lua 5.4.8: Lightweight, embeddable scripting language
- CMake: Cross-platform build system generator
- SCons: Alternative build system for complex dependencies
Build Requirements
- Compiler: GCC 7+, Clang 5+, or MSVC 2019+
- C++ Standard: C++17 or later
- Platform Support: Windows, Linux, macOS
- Godot Version: 4.0+ (GDExtension compatible)
Development Tools
- Python 3.6+: For build automation scripts
- Git: Version control and submodule management
- Visual Studio/VS Code: IDE support with C++ extensions
Build Configuration
Quick Start
To build the Lua Godot Bridge for your platform:
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/your-repo/lua-godot-bridge.git
cd lua-godot-bridge
# Initialize submodules
git submodule update --init --recursive
# Build for current platform
python build_addon.py
# Or build manually with CMake
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make -j$(nproc)Platform-Specific Builds
The project includes automated build scripts for different platforms:
# Windows build
.\build_addon.ps1
# Or use the batch file
.\build_addon.bat
# Build for specific target
python build_addon.py --platform windows --target releaseIntegration with Godot
After building, the extension can be integrated into any Godot 4 project:
# Enable the extension in project settings
# Add to project.godot:
[application]
config/features=PackedStringArray("4.2")
[gdextension]
load_once=true
singleton=false
symbol_prefix="godot_"
compatibility_minimum="4.2"
[libraries]
linux.debug.x86_64="res://addons/lua_bridge/bin/linux/lua_bridge.linux.template_debug.x86_64.so"
linux.release.x86_64="res://addons/lua_bridge/bin/linux/lua_bridge.linux.template_release.x86_64.so"
windows.debug.x86_64="res://addons/lua_bridge/bin/windows/lua_bridge.windows.template_debug.x86_64.dll"
windows.release.x86_64="res://addons/lua_bridge/bin/windows/lua_bridge.windows.template_release.x86_64.dll"